Whole Foods, Plant-Based Diet: A Path to Wellness
The whole foods, plant-based (WFPB) diet has gained significant traction in recent years as a powerful approach to improving overall health and preventing chronic diseases. This dietary pattern emphasizes consuming minimally processed plant foods while avoiding or limiting animal products and refined foods. The WFPB diet is not merely a passing fad but a scientifically supported eating strategy that has demonstrated numerous health benefits. As obesity rates continue to soar and chronic diseases become increasingly prevalent, many individuals and healthcare professionals are turning to this dietary approach as a sustainable solution for long-term wellness.

Key Principles and Foods
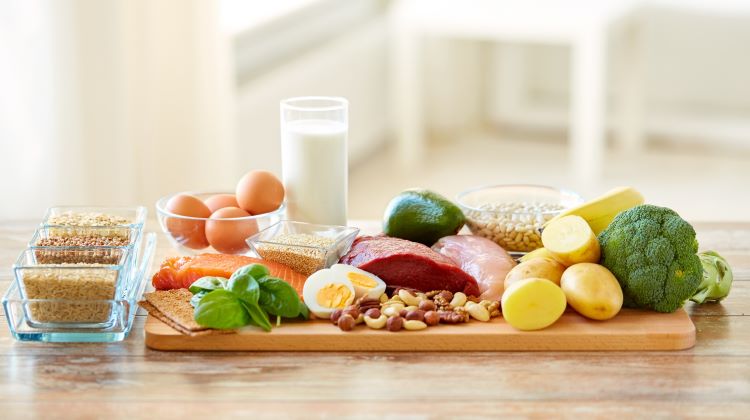
The WFPB diet is built on a few fundamental principles. First and foremost, it emphasizes consuming whole, minimally processed plant foods. This includes a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods are rich in essential nutrients, fiber, and phytochemicals that support optimal health. Processed foods, refined grains, added sugars, and oils are generally avoided or minimized. Animal products, including meat, dairy, and eggs, are either completely eliminated or consumed in very small quantities.
Health Benefits and Disease Prevention
One of the most compelling aspects of the WFPB diet is its potential to prevent and even reverse certain chronic diseases. Numerous studies have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The high fiber content and abundance of antioxidants in plant-based foods contribute to improved gut health, enhanced immune function, and reduced inflammation throughout the body. Additionally, many individuals who adopt a WFPB diet report significant weight loss, improved energy levels, and better overall well-being.
Environmental Impact
Beyond its health benefits, the WFPB diet has gained attention for its positive environmental impact. Animal agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. By reducing or eliminating animal products from the diet, individuals following a WFPB approach can significantly lower their carbon footprint. This alignment of personal health goals with environmental sustainability has made the diet particularly appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and has contributed to its growing popularity.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of a WFPB diet are well-documented, adopting this eating pattern is not without challenges. One common concern is ensuring adequate nutrient intake, particularly for nutrients typically found in animal products, such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. However, with proper planning and, in some cases, supplementation, these nutritional needs can be met on a plant-based diet. Another challenge is the social aspect of adopting a diet that differs from the mainstream. Many individuals find it difficult to navigate social situations, dining out, and family meals when following a WFPB diet.
Practical Implementation
Successfully adopting a WFPB diet requires careful planning and gradual implementation. Many experts recommend starting with small changes, such as incorporating more plant-based meals into one’s routine or participating in initiatives like “Meatless Mondays.” Educating oneself about plant-based nutrition, learning new cooking techniques, and exploring diverse plant-based ingredients are crucial steps in making the transition. Meal planning and batch cooking can help individuals stay on track and ensure a variety of nutrient-dense meals throughout the week.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
The rise of the WFPB diet has coincided with advancements in food technology and innovation. Plant-based meat alternatives, dairy-free products, and other plant-based substitutes have become increasingly sophisticated and widely available. These products can ease the transition for those accustomed to animal-based foods and provide convenient options for busy individuals. However, it’s important to note that many of these products are processed and may not align with the whole foods emphasis of a true WFPB diet.
Scientific Controversies and Debates
Despite its growing popularity and substantial evidence supporting its benefits, the WFPB diet is not without controversy in the scientific community. Some researchers argue that the complete elimination of animal products may not be necessary for optimal health and that lean meats and fish can be part of a healthy diet. Others debate the long-term sustainability of a strict WFPB diet for all individuals, considering factors such as nutrient absorption and individual metabolic differences. These ongoing discussions highlight the complexity of nutrition science and the need for continued research in this field.
In conclusion, the whole foods, plant-based diet represents a powerful approach to improving personal health and environmental sustainability. Its emphasis on minimally processed plant foods aligns with current nutritional recommendations and has demonstrated significant benefits in preventing and managing chronic diseases. While challenges exist in adopting this dietary pattern, the growing body of research, increased public awareness, and expanding market of plant-based options make it an increasingly viable and attractive choice for many individuals seeking to optimize their health and well-being.